The Census of Agriculture is the most complete account of U.S. farms and ranches and the people who operate them. Every Thursday USDA’s National Agricultural Statistics Service will highlight new Census data and the power of the information to shape the future of American agriculture.
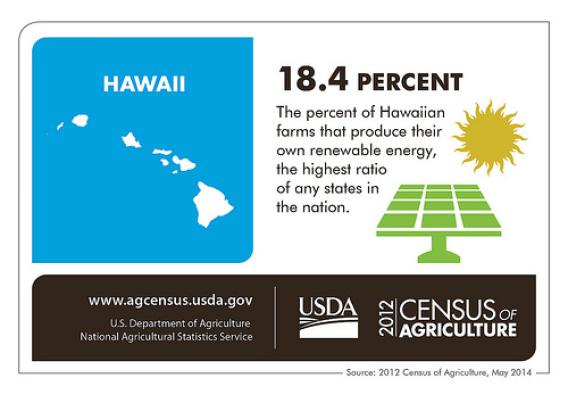
Hawaii may have only 7,000 farms, but our farming community is truly special and unique. For example, it is the only state in the United States where farmers grow taro, pineapples for commercial sales, and coffee. And if having such unique commodities isn’t enough, it is also the state that has the largest percentage of farmers and ranchers participating in renewable energy projects, according to the 2012 Census of Agriculture. More than 18 percent of our farms produce their own renewable energy on their farms.
The island environment is conducive to renewable energy production. Hawaii has abundant sunshine and steady trade winds which are favorable for investing in renewable energy systems. As a result many farms can set up photovoltaic panels and windmills to convert the sun and the wind to electricity.