This post is part of the Science Tuesday feature series on the USDA blog. Check back each week as we showcase stories and news from the USDA’s rich science and research portfolio.
What’s in the food we eat? Have you ever wondered if the foods past generations ate as children were more nutritious than the foods you now eat, or vice versa? Well, let’s take a look at the amount of nutrients available in foods for over 100 years!
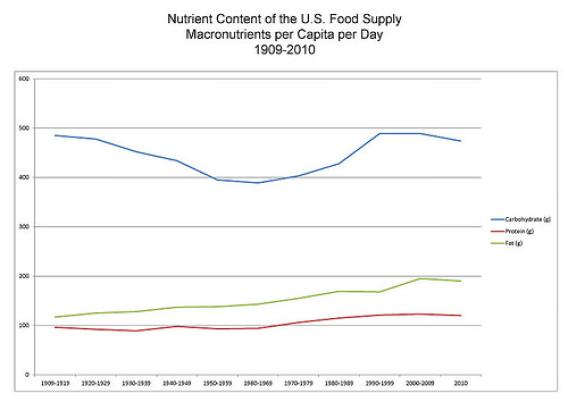
The Nutrient Content of the U.S. Food Supply is a historical data series beginning with 1909, on the amounts of nutrients available in the food supply for consumption (not nutrients consumed), on a per capita per day basis, as well as percentage contributions of nutrients by major food groups. The series provides data for food calories and the calorie-yielding nutrients which are protein, carbohydrate, and fat (total, saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and individual fatty acids); cholesterol; dietary fiber; 10 vitamins; and 9 minerals. Food supply nutrients are closely linked to food and nutrition policy, with prominence in areas related to nutrition monitoring, Federal dietary guidance, fortification policy, and food marketing strategies.